Cardiovascular risk factors

1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases
The most significant ones for their severity and frequency are:
- Brain vascular accident.
- Angina pectoris.
- Acute heart attack.
The arteries are the conducts where the blood circulates transporting the oxygen and nutrients necessary so that all the organs and muscles of the human body work properly.
Any disorder of the arteries will cause disorders to the corresponding area of the blood supply. The blockage of an artery causes no arrives food to cells and these can arrive at to die, its breakage causes an internal bleeding, its tightening a rise of the blood pressure, etc.
The heart, engine that moves everything this essential transportation for the life, can not stop, since the blood circulation is constant in order to be able to exchange products that it contains.
The heart beats in a half life of 80 years almost three billion of times. But we just remembered his when us aches, and it can that whether it is too afternoon. It is a machine that we must take care of so that it can give us the best quality of life possible.
Disorders of the arteries
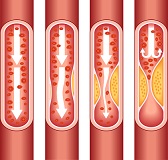
The cholesterol leaves accumulating between layers of the arteries, plate of atheroma, and as it increases this deposit leaves narrowing the arterial light which it causes that every time arrives less blood to its destination. The body starts to suffer, since needs more food. When this happens in the heart, this causes a heart attack or angina pectoris. To brain level you can produce a taponamiento for a thrombus that is given off of a plate of atheroma or you can break the artery causing a hemorrhage. In both cases a vascular brain accident will be produced.
The same process is observed here. The difference between angina pectoris and a heart attack is that the artery is not entirely blocked during angina pectoris so some blood can arrive.
Brain vascular accident (acute appearance symptoms)
- Paralysis of a limb or of everything the hemicuerpo.
- Difficulty to talk.
- Memory loss.
- Facial paralysis.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Loss of view of an eye.
- Difficulty for gait (lateralización).
Angina pectoris
- Precordial pain of intensity variable.
- It can irradiate to left arm, back or jaw, or not.
- It usually appears after carrying out an exercise, effort, stress, copious food, cold extreme.
- It disappears with the break.
- It disappears with nitroglycerin.
- It can happen unnoticed.
Acute heart attack
- Intense precordial pain, major weight.
- It can irradiate to left arm, back or jaw, or not.
- They can appear nauseas, vomits, throat irritation.
- It appears in a sharp way.
- It does not disappear with the break.
- Improvement but it does not disappear with nitroglycerin.
- Gravity and relocation sensation immediate.
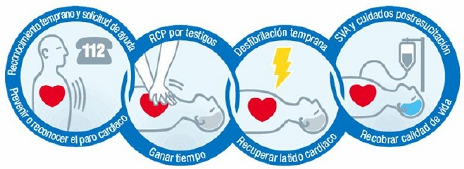
2. What to do in the event of angina pectoris, heart attack and cardiopulmonary arrest
What to do in the event of angina pectoris or heart attack
- Notify the emergency service: 112.
- Reassure.
- Accomodate in horizontal.
- Loosen any tight fastenings: tie, belt, etc.
- If sublingual nitroglycerin is had, to manage her.
- Manage aspirin 500 in the event of allergy.
What to do in the event of cardiopulmonary arrest
- Notify the emergency service: 112.
- Initiate manoeuvres of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (RCP).
- Starting for 30 heart compressions and two insuflaciones word-of-mouth in a repeated way.
- If defibrillator is had it is necessary to use it as soon as possible, since the survival decreases let alone time is taken in applying. In the first minute, the survival rate is > 95%. After 5 minutes, it is < 40%.
3. Risk factors
Risk factors are the causes that are known scientifically to directly affect the occurrence of these diseases. Usually is talked of non checkable factors and checkable factors, auque there are risk factors so-called emerging that they influence to cellular level: as the protein C reactive, the thickness of the intimate layer arterial, the fibrinogen or levels of calcium in the intimate one, among others.
Uncontrollable
- Age.
- Family history.
- Gender.
Controllable
- Cholesterol.
- Hypertension.
- Tobacco.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Obesity.
- Diabetes.
4. Uncontrollable risks

Non checkable risks do not depend on the person:
-
Age
To more advanced age major risk, owing to the fact that the heart and arteries age and if we do not have them care start to alter. -
Herencia genetics
Have progenitors that have had these illnesses involves a major risk of suffering by its daughters and children. -
Gender:
Men suffer more cardiovascular diseases that women. However in recent years, cardiovascular diseases that suffer women are graver.
The fact that women have started smoking means that they are more affected by cardiovascular diseases than ever before. The menopause also increases the possibility of cardiovascular diseases due to a decrease in the effect of oestrogens, the female hormone with cardioprotective effects.
The takeover of oral contraceptives, in women of more than 35 years with risk factors, increases the probability of suffering a cardiovascular disease. He owes consult with its medical staff.
5. Controllable risks


Checkable risk factors are those which you can personally control or with assistance of medical staff. The adoption of good habits can arrive at to reduce the probability of suffering a cardiovascular disease in more than 30%.
Cholesterol
The cholesterol is a substance that is found in person and animals, essential for the life for being the forerunner of the vitamin D and to synthesise various hormones, among others functions.
Cholesterol levels depend on the body's own production and external intake through food.
The cholesterol travels by the organisation of two ways mostly: with high density lipoproteins (HDL), or good cholesterol, for protecting of cardiovascular diseases and low density lipoproteins (LDL), or bad cholesterol, for promoting vascular diseases and cardiac.
We know that LDL cholesterol forms atherosclerotic plaques.
Total cholesterol values include two types of cholesterol, so it is important to always know what proportions we have of each one. A high HDL reduces the risk.
Correct values of lipids in blood:
Total Cholesterol: < 200 mg/dl
* Cholesterol - LDL: < 130 mg/dl
* Cholesterol - HDL: >50 mg/dl
Triglycerides: < 150 mg/dl
Foods rich in saturated fatty acids are those that contain most cholesterol.
Classification of fatty acids:
Saturated (high in cholesterol): bacon, butter and animal fat (skin of the chicken).
Unsaturated (low in cholesterol): olive oil, white, fished and walnuts meat.
Tobacco
More than 4,000 substances have been identified in cigarette smoke with the following characteristics: antigenic, pharmacologically active, carcinogenic, cytotoxic and mutagenic.
The nicotine alters vascular walls, increases the coagulation of the blood and it causes narrowing of the glasses.
Person passive smoker:
It has been demonstrated that the smoke that it goes out of the tip of the cigarette is that which contains more toxic substances and is that which breathes the person passive smoker.
There are studies that they demonstrate that if in a couple that convice joint one of the people smokes a daily package of tobacco at home, the other non-smoker person is as though it smoked one half, and therefore it is exposed to the same illnesses.
Children are major imitators, children smokers progenitors and daughters smokers. It is necessary to start to teach good habits to our children and daughters in order to be able to have adults and old men healthier and with finest quality of life.
It is known that in pregnant women the tobacco can be cause of abortions, children or girls of low weight and other alterations.
High blood pressure
Pressure made by the blood against the artery walls:
- It increases for several factors, many of them strangers but it is known that increases for the intake of salt, canned foods and carbonated drinks.
- It produces alterations in different bodies and systems.
- It can cause the slippage of a plate of atheroma and breakage of a glass.
- Standard values: maximum pressure < 130, minimum < pressure 85.
Sedentary lifestyle
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines it as follows: when less than 2.5 hours of moderate exercise or less than 1 hour weekly of intense exercise is carried out.
A lack of physical activity causes: excess of diet, rise of cholesterol, muscular and smaller decrease contributes of Or2.
A sedentary lifestyle is related directly with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, osteroporosis, high blood pressure, colon cancer, breast cancer, etc.
We can correct it by simply doing some exercise. What can we do?
- Walk 60 minutes per day, quickly.
- Go up and go down staircases.
- Use public transport.
- Do moderate sport at least three times a week.
- Avoid the intense sport of subsequent weekend and feast.
Obesity
- Rise of the volume of fat. There is an excess of contributes of calories with regard to fats that we spend, and this energy excess is deposited in the shape of carbon fat and hydrates.
- Fat is a deposit of toxic substances. Many contaminants are stored in the fat cells that act as a reservoir.
- Repercussion on organs. Weight gain has repercussions on all our organs which means that they have to work harder.
- Increase in cholesterol. When you do not burn calories, fat is stored and muscle mass is reduced.
Indexes for the calculation of the obesity
Body mass index: BMI (20-25 Kg/m2)
Abdominal perimeter: AP: <102 / 88 cm
Degrees of obesity
The Body mass Index (BMI) just takes into account the relationship of the weight with the height, not the amount of fat.
For this reason, does not serve in people that do sport of common form since the muscle weighs more than the fat and you would produce errors. Two people with the same height and same weight would have the same BMI if one is obese and the another one is athlete. This is owed to that the muscle weighs more than the fat.
Abdominal perimeter
Abdominal fat is known to be the fat that is related directly with cardiovascular diseases, which is why the abdominal perimeter measurement is a more trustworthy value than the BMI with regard to this type of disease.
It is considered that men should have an abdominal perimeter of less than 102 and women less than 88.
As you can observe, the diet is very significant as good habit since it influences in the majority of checkable risks. A good diet is basic to improve our health and quality of life.
Food
It is the conscious act of eating. We often eat because of what we see, not because we are hungry. We have replaced good eating habits for fast food and convenience foods.
Nutrition
It is the unconscious act, which the body really needs to live. In order to repair itself and work properly. What the body needs from everything that we eat is what it is formed of. Everything else is eliminated or accumulated in the form of fat or carbohydrates.
The use of nutrients corresponds to the energy expenditure of each person. The greater the activity, the higher the energy intake.
Food groups:
- Bread, cereals, rice and dough.
- Fruit and vegetables.
- Milk, meats, fishes and legumes.
- Fats and sugars.
It is recommended that a third of the dish is formed from group 1, another third from group 2, less than a third from group 3 and very little from group 4. And to drink between 1.5 and 2 litres of liquid a day.
The Mediterranean diet has been proven to be cardioprotective due to its ingredients. In 2011, it was appointed an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO due to its important benefits in cardiovascular protection. Olive oil, pulses, fruit, fish and nuts are some of the foods in this diet.
Olive oil
- 80% unsaturated acids.
- 14% saturated acids.
- Virgin and not refined.
- Rich in carotenes and vitamin And, that are antioxidants, and in poor fatty acids in cholesterol.
- A spoonful tureen is recommended a day of olive raw oil.
Fishes
- Omega 3: fat that it increases the HDL and it has effects cardioprotectores. Is found mostly in the blue fish (sardine, anchovy, salmon, etc.).
Fruits, vegetables, legumes, doughs, cereals and nuts
- Low glycaemic index: they release sugar slowly into the blood stream which helps to avoid diabetes.
- High in fibre: the fibre is one of the better preventions of Columbus's cancer, promotes drags the of all substances towards the exterior.
Wine
- Tannins: se find in the black grape and they have a stock anticoagulant and antinflamatoria.
- Resveratrol: substance that acts as a,natural anti-fungal agent for grapes. It is cardioprotective and is related with rejuvenation mechanisms.
- Moderate use of wine and beer in people that are usually drink has cardioprotective effects. Once the recommended doses are exceeded, the harmful effects outweigh the beneficial effects. People that do not drink should continue not to drink.
Antioxidants
These are substances that eliminate the free radicals produced in metabolic reactions due to excess calories and which are toxic for the cell. They are found in colourful fruits and vegetables.
- Carotenoids: carrot, spinach, tomato, melon, etc.
- Selenium: walnut, garlic and brócoli
- Vitamin E: cucumber, melon, strawberry, orange and lemon
- Zinc: pumpkin and nuts
- Quercetin: Green tea and grape
- Tannins: wine
As indicated by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (WCRF):
A good allowance can prevent
- 50% of breast cancers
- 75% of stomach cancers
- 75% of colon cancers
Eating between 3 and 4 servings of fruit and vegetables a day reduces the incidence of cancer by 20%.
A change in diet combined with giving up smoking means that between 60 and 70% of cancers will be avoidable.
6. Other cardiovascular risk factors

Alcohol
- The moderate consumer spending of came or beer, less than 30 gr. per day, increases HDL.
- The over-consumption, more than 30 gr. per day, promotes various illnesses' appearance.
- Is measured for units of drink (UB).
- One alcohol unit is equal to 8-10 gr. of raw spirit.
- The danger limit is 30 gr. of alcohol per day, 3 alcohol units for men, and 20 gr. of alcohol per day, 2 alcohol units for women.
- For people who like drinking, it is recommended not to drink more than two or three glasses of wine or beer per day. To the not drinkers, it is recommended that are still it. A glass of wine or beer is equal to 10 gr. of alcohol. A glass of distilled spirits is equivalent to 20 gr. of alcohol.
Stress
- Permanent tension state.
- Is not achieved to go out.
- It causes dysfunctional reactions.
- Demands exceed the capacity of response.
- Stress is a physiological reply of the body to what each person considers to be an external aggression or stressor. When we have a response for this aggression, the stress disappears. The problem is that stressors get increasingly difficult to find a solution for and not being able to find a solution is very tiring. As a result, we enter a phase of permanent stress that causes organic alternations such as tiredness, headache, depression, etc.
- Within our world, we live in several subworlds such as the family, work, society and the individual. Each subworld has its stressors and each one forces us to find solutions to overcome them.
- The illness, children or daughters, the mortgage, a removal, the work load, etc. they are examples of causes of stressors.
7. Set of rules for good habits

- Have a varied diet, rich in vegetables, cereals, legumes and fruits.
- Drink milk and derivatives skimmed.
- Drink daily 1.5 litres of water.
- Fats do not have to exceed 30% of total calories.
- Use raw olive oil.
- Consume moderately meat, to predominate the white meat on the red one, and to increase the consumer spending of fish.
- Avoid intake of alcohol > 30 gr/day.
- Avoid tobacco and stress.
- Carry out physical exercise.
- Sleep between 6 and 8 hours daily.