Coordinación de actividades empresariales

The contracting of works or services in the business field, regular practice currently, takes partner several companies' confluence or people self-employed workers in the same work centre, which it can cause because of the interaction of different developed activities and of inherent risks that each takes partners, situations in which the possibility of accident is seen aggravated, as also its potential consequences.
It is for this reason that the standard in risk prevention at work it dedicates special attention to these situations, in the article 24 of the law of risk prevention at work , and in its development in the Royal Decree 171/2004, establishing the need of carrying out a coordination of business activities to control those interactions and to guarantee that companies or concurrent self-employed workers people act in a coherent way to principles of the preventive action and they apply correctly work methods.
You know what figures exist in the coordination of business activities?
Although the duty to cooperate applies equally to all the undertakings and self-employed individuals involved, the specific obligations for each one vary depending on their role in the concurrence situation (relation to the place where the project is carried out, type of work contracted, position in the subcontracting chain, etc.). Check them out below.
Do you do anything or simply file documents?
 Although BAC's purpose is straightforward and specific, it often turns into a mere exchange of documentation between the parties with no practical and effective contribution to the goal initially pursued and thus into a sterile and unproductive process which is just going through the motions to meet statutory requirements. The most common contributing causes are:
Although BAC's purpose is straightforward and specific, it often turns into a mere exchange of documentation between the parties with no practical and effective contribution to the goal initially pursued and thus into a sterile and unproductive process which is just going through the motions to meet statutory requirements. The most common contributing causes are:
- Highly defensive BAC procedures exclusively designed to demonstrate legal compliance with a predominance of:
- Piling up documentary evidence, including information which has nothing to do with health and safety in a concurrence situation.
- No analysis of the information received, meaning that no specific measures are taken based on its content to help monitor risk situations.
- Piling up documentary evidence, including information which has nothing to do with health and safety in a concurrence situation.
- BAC is seen in isolation as something completely disconnected and detached from the work prompting it. BAC is usually seen as a one-off management task to be done prior to the start of the project and not as a continuous and simultaneous process during its rollout. In most cases, this entails:
- There are no means of coordination, or where they do exist, they are inappropriate for the type of project and its features.
- There is no follow-up or supervision of the progress of the work, which is in stark contrast to the effort put into compiling documents.
How can you achieve effective BAC?
BAC should be approached as a continuous process geared towards mainstreaming health and safety at every stage of the project, starting from when the need to outsource work or services is identified and ending with the conclusion of the subcontracting relationship, and which should result in tangible, applicable and effective measures to help enhance health and safety conditions in concurrent work.
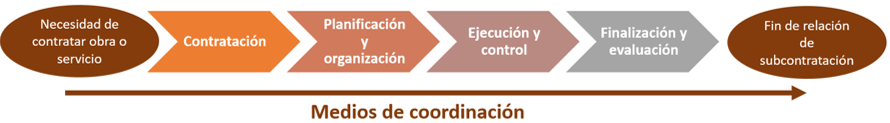
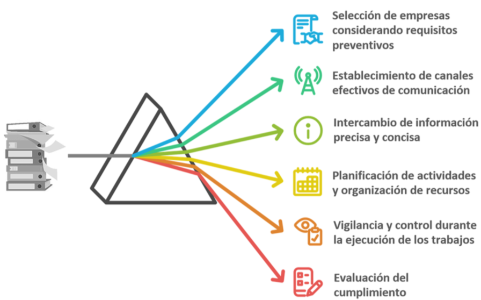
This involves putting in place appropriate coordination mechanisms fostering flexible and continuous communication and exchange of information between the parties and ensuring each of them (incumbent and concurrent companies) proactively and responsibly undertake their assigned tasks at each stage. Health and safety in the concurrence situation is a matter for all parties involved as the shortcomings or disengagement of one party can have an impact on the others.
To help bring about a paradigm shift towards business activity coordination focused on the result and not only on demonstrating legal compliance, Mutua Universal has a short best practice guide which outlines the stages of the process, the role to be played by the incumbent company, the concurrent companies and the main company when there is one, coupled with the flows of information between them.
Remember
 The coordination of activity business studies:
The coordination of activity business studies:
- It is compulsory in the situations of company or person confluence freelance workers (Article 24 LPRL).
- It requires of the shared responsibility of all parts and pursues to guarantee the protection of people that they participate in the works.
Although the normative framework is necessary to regular and to establish some minimum guidelines, this should not become exclusive star, nor efforts and resources must be monopolised by the evidential generation of the legal requirement.
You do not allow that the EAC is only documentation.
Would you like more information?
Get in touch with your technician/to of Mutua Universal's prevention for an advice in any related question, enquiry the legislation and technical documents, or preventive obligations in EAC if you are a SME.

