Travel: what to bear in mind.
Lee the complete content in Infermera Virtual
1. The customised advice

Every trip supposes an only and different experience for the person that it does. Therefore, advice and recommendations to travel with health vary according to characteristics of the trip and the particularities of the person that it travels, as its health history and its life situation.
2. Characteristics of the trip
Aspects that determine the characteristics of a trip include the destination, the duration, the type of accommodation, the route and conditions of the trip, the type of contact with the town, the period of the year, the means of transport, the practice of risk activities and the administrative and health requirements.
Destination:
Necessary to maximise is considered precautions in trips to:
- Rural areas or isolated, with poor hygienic conditions or with difficulty of access to a healthcare if necessary.
- Countries or areas with severe climatic conditions: heat or cold intense, high humidity, or sharp changes of the environmental temperature during the day and night.
- Countries or areas with armed conflicts or an unstable political situation.
Duration:
It determines the time that the person is in touch with certain health risks, that are current, especially, in developing countries.
Type of accommodation, route and conditions of the trip:
Necessary to maximise is considered precautions in the event of trips that they suppose:
- accommodations with poor hygienic conditions;
- routes for rural areas or isolated, with difficulty of access to healthcare.
Type of contact with the town:
Necessary to maximise is considered precautions in case:
- Have an intense contact with the local people in areas with illnesses of contagion from person to person, as it is the case, for example, of aid workers or volunteers that they work very directly with the inhabitants of a place.
- They take place works in touch with sick people, armed conflict or natural disaster refugees, or tasks that involve the contact with animals, for the risk of contagion of some illnesses.
Time of the year
Necessary to maximise is considered precautions if is had to travel to areas with severe climatic conditions: heat or cold intense, and/or high humidity.
Means of transport
It can cause health risks, as, for example, the syndrome of the economy class in trips in plane, the dizziness in trips by boat or traffic accidents in trips in car.
Risk activity practice
Certain risk activities, including the sport ones, can be part of the collection of activities planned or be the main reason of a trip. They require a special feature activities of mountain and subaquatic activities.
Administrative and health requirements.
According to the country or the area that is visited, can be necessary:
- Consult the health centre or the centre of international vaccination to plan with time the administration of the compulsory vaccinations and/or recommendable according to characteristics of the trip and of the person that it travels.
- Have visas or of permissions of entrance or internal route, according to the country or the area that is wanted to visit, that you can manage in the country of destination or in that one of origin.
3. The personal aspects of the health
It is related to current or previous health problems, acute or chronic; allergies to medications, to foodstuffs or to environmental factors; the case history of vaccinations and the physical or mental limitations of the person that it travels.
Illnesses or health problems, acute or chronic
They make reference to health problems or to illnesses that the person has had throughout the life or that it has at the time of to undertake the trip. Following on from this, also is significant to take into account if the person follows some processing and, if is thus, to know which. This can condition advice of specific health for its situation.
Allergies to medications, to foodstuffs or to environmental factors (pollen, dust, mites, etc.)
These allergies can require a preparation and some advice of health specific.
Case history of vaccinations of the person
It is necessary to know the previous case history of universal vaccinations, as, for example, that one of lockjaws in adults to avoid health problems if injuries are produced during the trip. In the case of children, he owes have in account the calendar of child vaccinations to avoid usual illnesses during the childhood and to adjust it to the vaccinations necessary to the trip that is wanted to do.
Physical or mental limitations
These limitations can require logistic or instrumental adjustments during displacements or the accommodation, or the need of a companion person
4. How to avoid dangers and to prevent risks
Do a trip can be a nice activity, but also can entail health risks. Look after the health is a responsibility of the person that it travels. For this reason, is advisable:
- Before travelling, to know which are the country's health precautions or of the area that is wanted to visit: prevention measures of health risks, vaccinations and the prevention of the malaria or malaria, always with a previous health advice customised.
- Learn more about possible agreements health with other countries, in the event of accident or illness during the trip.
- Contract a health insurance with a suitable coverage to the type of trip that is done, to the duration and to the destination.
- Contact, in the country of destination, with the embassy or with the consulate of the home country; above all, in areas with political conflicts, in long-term trips or in placements in isolated areas.
- Take decisions to travel in a healthy way taking into account the different life situations of the people: phases of the life cycle, the pregnancy, to have a chronic disease or to have a disability.
5. Vaccinations
Vaccinations allow preventing some illnesses and they complement prevention measures of health problems. Therefore, is significant to receive them when they are necessary to protect of these illnesses and being able to enjoy, thus, of a trip with health.
It is always advisable a planning with time, if is possible, of a month earlier of the trip, in order to be able to manage indicated vaccinations, according to the general factors that condition the customised advice, characteristics of the trip, the history of health and the situation of life of the person that it travels.
He owes have always current that the vaccination does not substitute the need of following preventive measures of necessary health problems in every situation.
General guidelines
Below, vaccinations are described that are recommended of general way to the people that they travel.
Lockjaws and diphtheria
Lockjaws is a severe illness of worldwide distribution caused by a bacterium that is found in the earth; se passes on via injuries. The diphtheria is an illness of worldwide distribution that it can be serious; se passes on for contact with sick or carriers people of the illness. There is a combined vaccine for two illnesses and is recommendable for any trip or destinación.
Specific recommendations
Below, recommendable or compulsory vaccinations are described according to characteristics of the trip, the case history of health and the situation of life of the person that it travels. They are especially necessary in the trips to developing countries.
Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Typhoid fever, Yellow fever, Meningitis meningococia A-C and To, C, And, W-135, Rage, Japanese Encephalitis, Pneumococcus, Cholera, Flu, Poliomyelitis, Central European Encephalitis, Triple vírica (Measles, Rubeola and Mumps).
6. Malaria and malaria
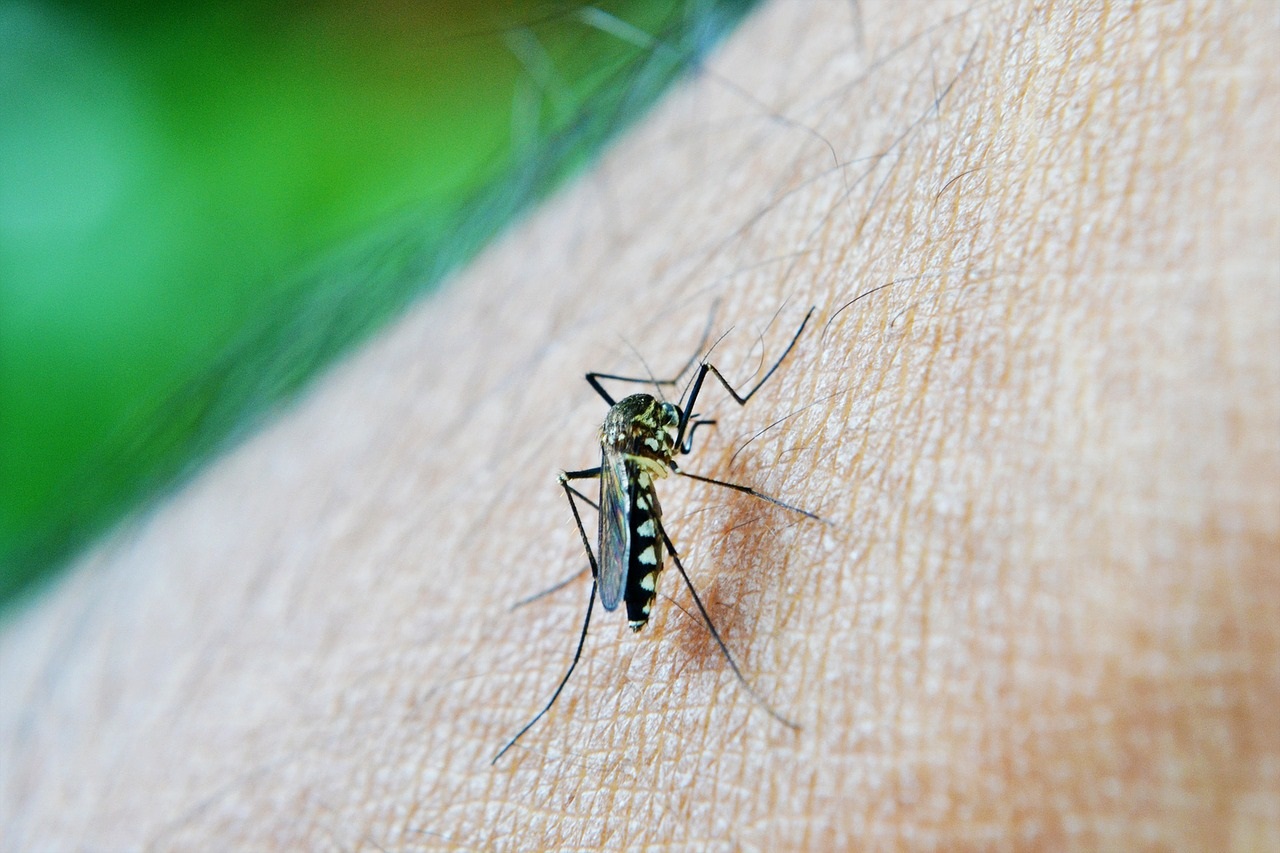

The malaria or malaria is a more common illness in some developing countries, of the tropical area and subtropical of Africa, of Asia, of Central America and South America; se passes on for the insect bite of a mosquito, that it usually chops of the atardecer until the early morning.
People that they travel to endemic areas or countries (countries where there are an endemic disease) must apply corresponding measures to prevent her, since, if it does not be suitable way, can have serious consequences.
It suits to follow recommended preventive measures to avoid mosquito's insect bites, although the pharmacological prevention of the malaria has been done.
General guidelines.
- It is necessary to customise prevention measures according to characteristics of the trip: the destinación, the duration, conditions, the climatic period and the characteristics of the person.
- It is necessary to follow prevention measures of the insect bites of mosquito to avoid the contagion of the illness.
- He owes use the preventive medication (quimioprofilaxis antimalarial) more suitable according to characteristics of the trip and those of the traveller, according to customised recommendations for a nurse or a skilled practitioner.
- There are different medications preventive and the dose varies according to the type of medication: ones are managed with weekly doses and others, with daily doses. All have to start to take before entering an area at risk of malaria or malaria and they must continue taking during the placement and when going out of the area at risk of the illness.
7. It prepares the suitable medicine cabinet!
The medicine cabinet contains medications, the material of cures, reports and/or the medical archive that it can be necessary at one point to attend any health problem, in general of slight type, that it can have the traveller.
Medications and basic material for emergencies:
- Painkiller/antithermal for the pain or the fever;
- Anti-inflammatory for pains of more intensity or inflammations;
- Antidiarrheal by the time the diarrhea is not accompanied of fever and always as a complement of the oral hydration;
- Envelopes of rehidratación oral, that they must dissolve in a litre of water, in the case of diarrheas or vomits (you can prepare of homemade way dissolving, in a litre of water, six teaspoons of sugar, one of salt, one of lemon baking soda and juice);
- Oral antihistamine for allergic reactions or chopped of insects;
- Medications for to the dizziness in trips by boat or for people with trend to the dizziness in different means of transports;
- Basic material of cures (plasters, lints, antiseptic to disinfect injuries).
- Thermometer.
- Insect repellents.
- Cliched product for the skin, with a component of antihistamine or with ammonia, to reduce the itch subsequent to the chopped ones.
- Solar protective cream.
In the event of having a chronic disease or in other special health situations:
- Explanatory medical report in the language of the country of destination or of the countries of transit;
- Twice the medication, distributed in different places of the luggage, in case a part was lost, in the event of following a drug therapy.
General, to take medications or the material that the person knows to use.
In the case of travel in a group, to take an only medicine cabinet, with one or more people that they are responsible for him.
Use medications always following indicated recommendations in the leaflet specific corresponding.
